In today's increasingly digital world, IT security has become a crucial concern for businesses. With the proliferation of online threats, protecting sensitive data and preventing cyber attacks are major issues. That's where business firewalls come in. In this article, we take an in-depth look at the role and functions of this essential component of IT security, as well as the criteria to take into account when choosing hardware and an installation/operator partner.
WIFIRST FIREWALL AS A SERVICE SOLUTION
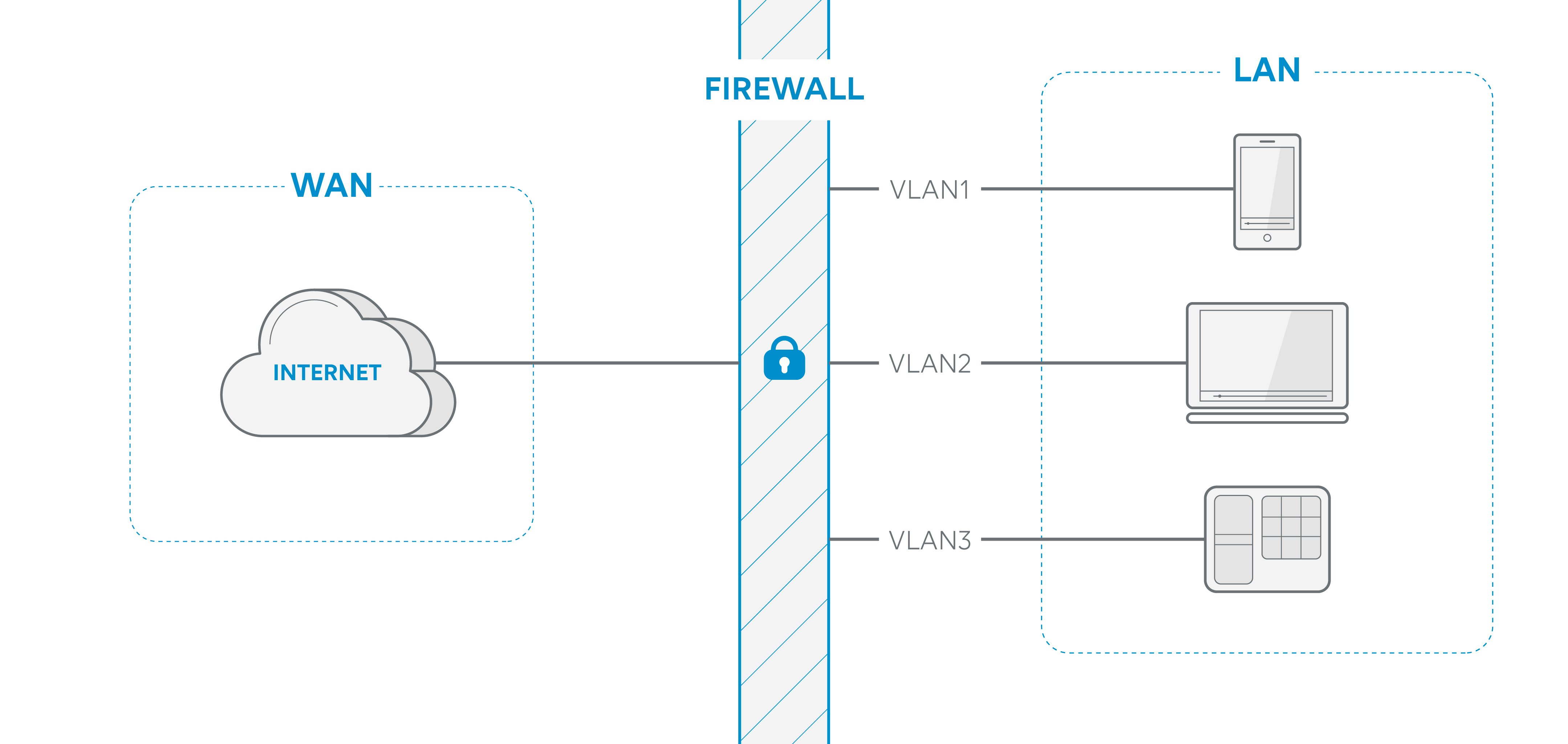
I. Understanding business firewalls
1.1. What is a firewall?
A firewall is a network security device designed to protect a computer network against external threats. It acts as a virtual barrier between the company's internal network and the Internet, filtering incoming and outgoing traffic to ensure that only authorised items can pass through.
1.2. Types of firewalls
There are several types of business firewalls, each with its own advantages and disadvantages:
- Hardware firewall: A physical device installed between the company's internal network and the Internet connection. Hardware firewalls offer robust protection, but can be expensive and require regular maintenance.
- Software firewall: Programs installed on servers or individual computers. They are more flexible than hardware firewalls, but can be less effective against network threats.
- Cloud-based firewall: Hosted on remote servers managed by security providers. Easy to deploy and manage, but their effectiveness depends on the quality of the service provided by the provider.
1.3. Key features of business firewalls
A business firewall is much more than a simple shield. It offers a range of essential functions to guarantee IT security:
- Network filtering: Examines every data stream entering or leaving the network and blocks those that do not comply with predefined security rules.
- Protocol inspection: Monitors communication protocols (such as TCP, UDP, ICMP) to detect suspicious behaviour.
- Application management: Identifies specific applications used on the network and applies security policies accordingly.
- VPN (Virtual Private Network): Provides secure access to remote networks via VPN connections.
- Intrusion prevention: Includes detection and prevention mechanisms to stop malicious activity.
- Logging and reporting: Records security events to make monitoring and analysis easier.
II. Evaluation criteria for choosing a business firewall
Choosing a business firewall is a crucial decision, as it determines the level of security of your network. Here are the criteria to take into account when evaluating the options available:
2.1. Specific business requirements
Before choosing a firewall, it's essential to understand the specific needs of your business. Ask yourself the following questions:
- What is the volume of traffic on your network?
- What types of threats is your company exposed to?
- What applications and services do you use regularly?
Once you have a clear vision of your needs, you can look for a firewall that meets them.
2.2. Performance
Performance is a key factor, especially if you have a lot of network traffic. Make sure the firewall you are considering can handle your business load without sacrificing connection speed.
2.3. Scalability
Is your business growing? Make sure your firewall can grow with you. The ability to add additional features or modules is a valuable asset.
2.4. Ease of management
An effective firewall needs to be easy to manage. Look for a user-friendly interface and remote management features to simplify configuration and monitoring.
2.5. Security features
Make sure the firewall offers a wide range of security features, such as intrusion detection, content filtering and protection against malware.
2.6. Updates and support
Security is constantly evolving, so it's essential to choose a firewall with support for regular updates to stay protected against new threats.
The main equipment manufacturers on the market are: Fortinet, Cisco, Forcepoint, Huawei, and Juniper.
III. Choosing the right installer/operator partner
Choosing the right firewall is a crucial step, but just as important is choosing the right installer/operator partner. Here are a few criteria to consider:
3.1. Experience and expertise
Look for a partner with solid experience in setting up business firewalls. Ask for references and check their expertise.
3.2. Compatibility
Make sure the partner has experience with the type of firewall you have chosen. They should be able to configure it correctly to meet your specific needs.
3.3. Technical support
The quality of technical support is essential. Check the coverage hours and escalation process.


